 The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recently released the latest draft of its annual Greenhouse Gas Inventory (GHGI), showing that methane emissions from oil and natural gas systems continue to fall at the same time production has continued to gradually increase.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recently released the latest draft of its annual Greenhouse Gas Inventory (GHGI), showing that methane emissions from oil and natural gas systems continue to fall at the same time production has continued to gradually increase.
The report says that methane emissions from natural gas systems have decreased 18.6 percent since 1990 largely due to a decrease in emissions from transmission, storage, and distribution. The positive trend numbers show that 2015 natural gas system methane emissions are 1.3 percent below 2005 levels and 1.1 percent below 2011 levels.
Methane emissions from natural gas systems have dropped while production has skyrocketed. In 2015 natural gas production was 52 percent higher than 1990 levels, 50 percent higher than 2005 levels and 18 percent higher than 2011 levels.
Industry efforts to reduce methane emissions have helped the U.S. reduce overall methane emissions by 16.7 percent since 1990, according to the EPA, and enteric fermentation has replaced natural gas as the top source of anthropogenic methane emissions.
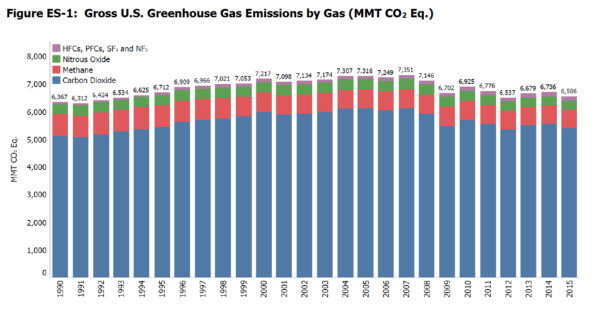
Increased natural gas use continues to drive down greenhouse gas emissions. EPA data shows overall CO2 emissions continue to plummet, as carbon emissions are down 11.7 percent from 2005 levels and 2.7 percent from 2014.
EPA credits natural gas use for electrical generation as the main contributor toward the sharp reduction in carbon emissions.
