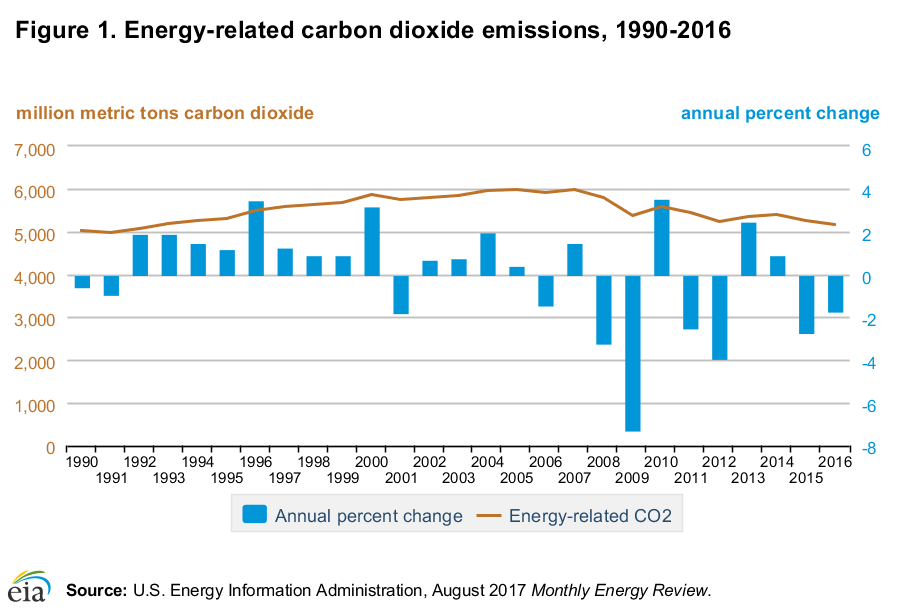
According to the EIA, 63 percent of energy-related carbon emissions reduction in 2016 can be credited to the utilization of cleaner-burning natural gas for electricity generation.
Data from the EIA shows that the switch to natural gas-fired electricity generation continues to drive down overall U.S. energy-related GHG emissions. From 2005 to 2016, U.S. electricity generation grew by one percent while power plant CO2 emissions fell 24 percent.
The EIA report notes:
“Of this total, 2,007 MMmt can be attributed to the shift in fossil fuels to natural gas, and 1,169 MMmt can be attributed to the increase in non-fossil generation sources.”
From 2005 to 2016, natural gas electricity generation increased from 19 to 34 percent of total U.S. electricity generation and was responsible for 63 percent of total power plant carbon emission reductions.